The Ultimate Guide to Your Tech Stack in 2025: A Founder's Roadmap to Long-Term Success
Hello, I'm Dillon Hughes. For the last seven years at Evietek, I've had a front row seat to the magic that happens when a brilliant idea meets the right technology. I started my journey from the ground up, learning to build digital solutions that truly resonate with people. It's not about chasing trends; it's about finding what genuinely fits. Through my blog, I want to pull back the curtain on these complex topics and give you practical insights.
Did you know that poor technical decisions are a major contributor to why many promising startups ultimately fail? It's a scary thought! As a founder, you're juggling a million things, and the term "tech stack" might sound like just another piece of jargon you're supposed to understand. But here's the secret: Your technology stack isn't just for your developers. It's the very DNA of your business the carefully selected collection of programming languages, frameworks, software tools, and services that bring your vision to life. Getting it right from the start impacts everything from your speed to market and ability to scale to your power to attract top engineering talent. Feeling overwhelmed? Don't be! This guide will break down everything you need to know, transforming you from a confused founder into a confident leader ready to make the right call for your company's future.
Key Takeaways
What a Tech Stack Is: Think of it as the DNA of your application. It's the specific combination of programming languages, software, frameworks, and tools your team uses to build and launch your product.
It's a Core Business Decision, Not Just a Tech One: The tech stack you choose directly impacts your app's speed, your ability to handle growth (scalability), your overall budget, and your power to attract skilled developers.
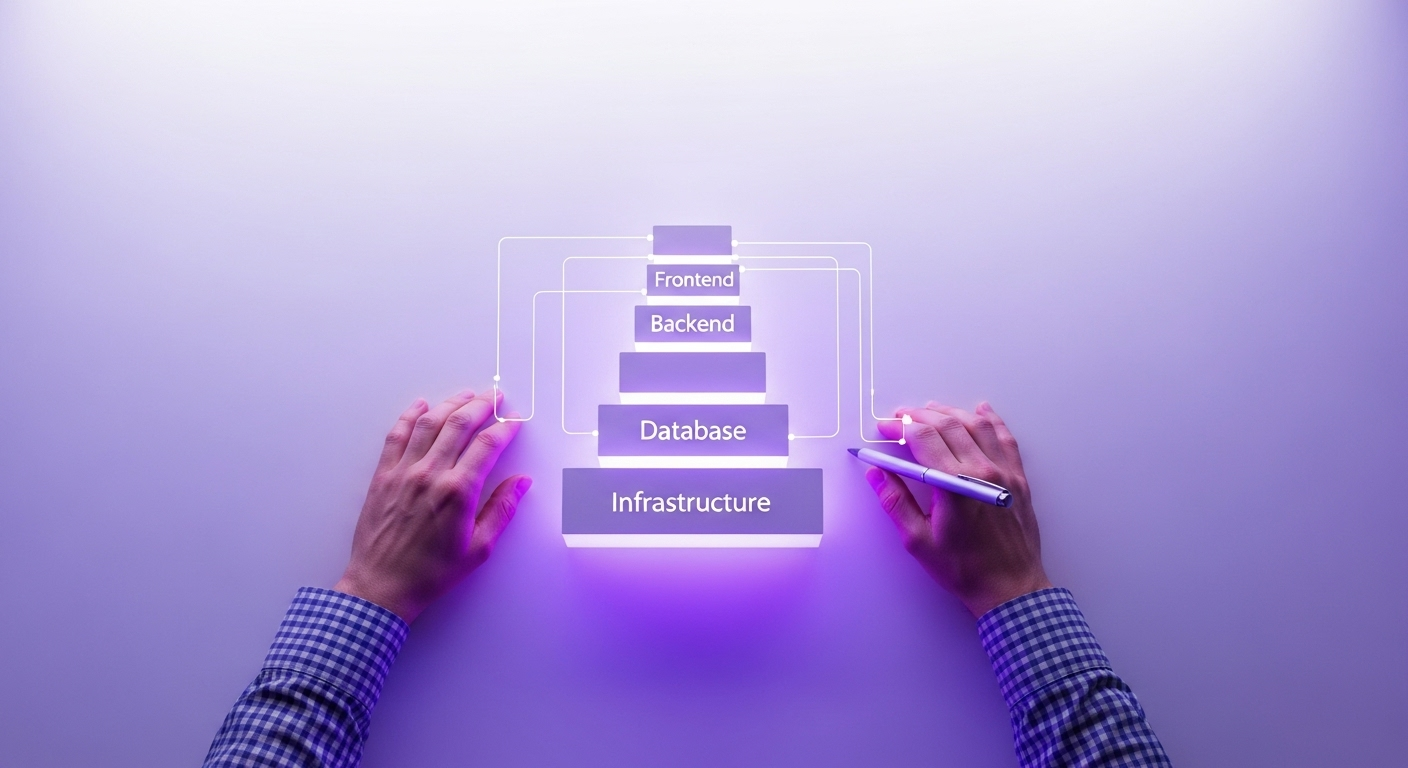
Understand the Four Key Layers: Every stack is built on four pillars: the Frontend (what the user sees), the Backend (the engine room and logic), the Database (where data lives), and the infrastructure (where your app is hosted).
Focus on "Right," Not "Best": There is no single "best" tech stack. The right choice depends on your project. A JavaScript-based MERN stack is great for modern web apps, while a Python/Django stack excels at data-heavy applications.
Avoid Costly Founder Mistakes: Steer clear of choosing a technology just because it's new and trendy. Don't over-engineer your initial product, and always make sure you can actually find and afford developers for the stack you choose.
Your Goal is a Scalable MVP: Your primary focus should be on getting a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to market. Choose a tech stack that allows you to do this efficiently while still being able to scale as your startup succeeds.
What Exactly is a Tech Stack? (Let's Break It Down)
Let's demystify this concept with an analogy I love to use. Think of building a house. Your tech stack is the complete set of materials and tools you use to construct it. You can't just throw random parts together and expect a stable home. You need a solid foundation, a sturdy frame, functional plumbing and electrical systems, and finally, the paint and finishes that people see. Your software application is no different.
- A Simple Definition: A tech stack, or technology stack, is the combination of technologies a company uses to build and run an application or project. It's the complete toolkit your development team uses.
- The Core Components Explained: Every web development stack has a few key layers that work together.
- Frontend (The User Facing Layer): This is everything your user sees and interacts with directly in their browser. This is the interior design of your house. We're talking about the layout, the colors, and the interactive elements. The core frontend technologies are HTML for structure, CSS for styling, and JavaScript for interactivity. Modern applications often use powerful JavaScript frameworks like React, Vue.js, or Angular to build complex, dynamic user interfaces.
- Backend (The Server-Side Engine Room): This is the part of the application that users don't see. It's the plumbing, wiring, and foundation that make the house functional. The backend handles all the business logic, communicates with the database, manages user authentication, and processes data. Common backend programming languages and frameworks include Node.js, Python with Django or Flask, Ruby on Rails, and Java.
- Database (Your Business's Brain): Your application needs a place to store and retrieve information, from user profiles to product inventory. This is your database. It's the secure filing cabinet of your business. There are two main types. SQL databases like PostgreSQL and MySQL are structured, like spreadsheets with rows and columns. NoSQL databases like MongoDB are more flexible and handle unstructured data, like documents.
- Infrastructure (The Foundation): This is the land and utilities your house is built on. Your application needs to live somewhere. This layer includes servers, data storage solutions, and the network that delivers your app to users. Today, most founders rely on cloud infrastructure providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or Microsoft Azure. This layer also covers DevOps tools for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), which automate how your code gets deployed.
Why Your Tech Stack is a Cornerstone of Long-Term Success
Many founders I talk to initially see the tech stack as a purely technical decision, something to delegate to their first engineering hire. This is a huge mistake. Your choice of an application stack has profound business implications that will echo for years.
- The Need for Speed (and Performance): In the digital world, speed is a feature. A slow, clunky application will frustrate users and send them running to your competitors. A well-chosen stack, built with performance in mind, ensures your pages load quickly and interactions are smooth. This directly impacts user satisfaction and conversion rates.
- Scaling for Tomorrow's Growth: What happens when your user base grows from one hundred to one hundred thousand? A scalable tech stack can handle this increase in traffic and data without crashing or slowing down. A poor choice here could mean a complete and costly rebuild right when your business is taking off. Thinking about a microservices architecture from the start can prepare you for this.
- The True Cost of Development: Your stack influences more than just performance. It dictates your budget. The cost to build a tech stack isn't just about software licenses. It's about how quickly your team can build with it and how easy it is to maintain. Popular, well documented technologies have large communities, meaning problems get solved faster and you spend less on development hours.
- Attracting and Retaining Top Talent: The best engineers want to work with modern, exciting tools. Your tech stack is a recruiting tool. A modern tech stack featuring languages like Python or frameworks like React.js can make your company far more attractive to top candidates. Conversely, an outdated or obscure stack can be a major red flag for skilled developers.
How to Choose the Right Tech Stack for Your Startup
So, how do you make the right choice? It's about asking the right questions and aligning the technology with your business vision. It's not about finding the "best" stack, but the right stack for you.
- Step 1: Analyze Your Project's Core Requirements:
- First, define what you are building. Is it a simple marketing website, a complex SaaS platform with real time data processing, or a mobile app tech stack for iOS and Android?
- List the absolute essential features for your minimum viable product (MVP). Simplicity is key at the start.
- Step 2: Consider Your Budget and Time to Market:
- Evaluate the costs associated with different tools. Open-source software is free to use but may require more setup and maintenance expertise.
- How fast do you need to get to market? Some full stack development frameworks are designed for rapid application development, which can be a huge advantage.
- Step 3: Evaluate the Talent Pool and Ecosystem:
- Look at the job market. How easy and expensive will it be to find developers proficient in your chosen technologies?
- A strong ecosystem with good documentation, active communities, and a wealth of third-party libraries will dramatically speed up your development process.
- Step 4: Think About Scalability from Day One:
- While you don't need to build for Google's scale on day one, you should choose technologies known for their ability to grow. Select a database and backend architecture that won't become a bottleneck as you succeed.
Popular Tech Stack Examples for 2025 (And Who Uses Them)
To make this more concrete, let's look at some popular tech stacks you'll see in the wild. A tech stack diagram can be a great way to visualize these components.
- The MERN/MEAN Stack (JavaScript Everywhere):
- Components: MongoDB (Database), Express.js (Backend Framework), React/Angular (Frontend Framework), Node.js (Backend Environment).
- Best for: Building comprehensive web applications where you want to use a single language (JavaScript) across the entire stack.
- Example: Companies like Netflix and Uber have famously used elements of this stack for their dynamic, high traffic platforms.
- The LAMP Stack (The Tried-and-True Workhorse):
- Components: Linux (Operating System), Apache (Web Server), MySQL (Database), PHP (Programming Language).
- Best for: Content management systems and e commerce platforms. It's incredibly stable and has a massive community.
- Example: This is the stack that powers a huge portion of the web, including WordPress.
- Python & Django/Flask Stack:
- Components: Python with its powerful frameworks Django or Flask, often paired with a database like PostgreSQL.
- Best for: Applications that are heavy on data, machine learning integrations, or scientific computing. Python's clean syntax makes development fast.
- Example: Giants like Instagram and Spotify rely on Python for its data processing power and speed of development.
- Serverless Stacks:
- Components: This is more of an architectural approach, using cloud services like AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, or Azure Functions.
- Best for: Applications with unpredictable traffic patterns. You only pay for the compute time you use, making it incredibly cost effective and infinitely scalable.
- Example: A great choice for startups building with a microservices approach who want to keep infrastructure costs low initially.
5 Common (and Costly) Mistakes Founders Make With Their Tech Stack
Over the years, I've seen some recurring patterns, some technical debt traps that are easy to fall into. Avoiding them will save you a world of headaches.
- Mistake 1: Chasing the "Hype": A new JavaScript framework is released every week, it seems. It's tempting to pick the newest, shiniest tool. Resist this urge. Choose mature, stable technologies with strong community support unless you have a very specific, compelling reason not to.
- Mistake 2: Over Engineering the MVP: Your first product doesn't need to handle a million concurrent users. Build a simple, robust stack that allows you to launch quickly, get user feedback, and iterate. You can always evolve your stack as you grow.
- Mistake 3: Ignoring the Talent Market: Picking an obscure language might seem cool, but it becomes a nightmare when you need to hire developers. You'll face a tiny talent pool and sky high salary expectations. Stick to mainstream technologies for your core product.
- Mistake 4: Not Planning for Data: The database is often an afterthought for non technical founders, but it's the heart of your application. Choosing the wrong type of database or designing it poorly early on can lead to massive performance issues and a painful migration process down the line.
- Mistake 5: Fear of Outsourcing/Advisors: If you don't have a technical co founder or a Chief Technology Officer (CTO), please get advice. A few hours with a tech stack consultant or a fractional CTO can save you hundreds of thousands of dollars in costly mistakes.
Conclusion
Choosing your tech stack is one of the most foundational decisions you will make as a founder. It's so much more than a list of technologies; it's a strategic business choice that will define your product's potential, your team's efficiency, and your company's ability to grow for years to come. Don't get paralyzed by the options! By focusing on your core business goals, understanding the trade offs, and planning for the future, you can build a powerful technology stack that doesn't just support your vision but actively accelerates it. Now, go build something amazing.
Quick Answers to Your Tech Stack Questions
A tech stack is the collection of software tools and programming languages used to build a web or mobile application. Think of it as the set of building materials for a digital product.
No, SQL (Structured Query Language) is not a tech stack by itself. It is a language used to manage and query data within a relational database, which is one component of a larger tech stack.
A typical web tech stack includes four core components: a frontend framework for the user interface, a backend programming language and framework for server logic, a database for data storage, and infrastructure for hosting.
Salesforce is more accurately described as a SaaS (Software as a Service) platform. While it has its own underlying technology, you typically build on Salesforce rather than building a custom application with it as your core stack.
Stacks utilizing JavaScript frameworks like React or Vue.js on the frontend and Node.js or Python on the backend remain in very high demand. There is also a growing demand for developers with experience in serverless architecture and cloud infrastructure like AWS.
Popular examples include the MERN stack (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js), the LAMP stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP), and a Python stack (Python with Django/Flask and PostgreSQL).
On a resume, "tech stack" refers to the specific programming languages, frameworks, databases, and tools a candidate is proficient in. For example, a developer might list "MERN Stack" or specify skills like "React, Node.js, AWS, PostgreSQL".
A tech stack diagram is a visual representation showing how the different layers of technology (frontend, backend, database, etc.) connect and interact within an application.
Python is a programming language, not a complete tech stack. It is a very popular choice for the backend component of a stack, often combined with frameworks like Django or Flask and a database.
The most popular tech stacks currently are JavaScript based stacks like MERN or MEAN, the classic LAMP stack, and Python based stacks. The choice depends heavily on the specific project requirements.